Technical architecture
A technical perspective on how the knowledge graph fits into your existing and developing technical architectures. BMJ focuses on collating evidence based knowledge so that you focus on supporting your clinicians and patients with compelling digital tools with embedded evidence.
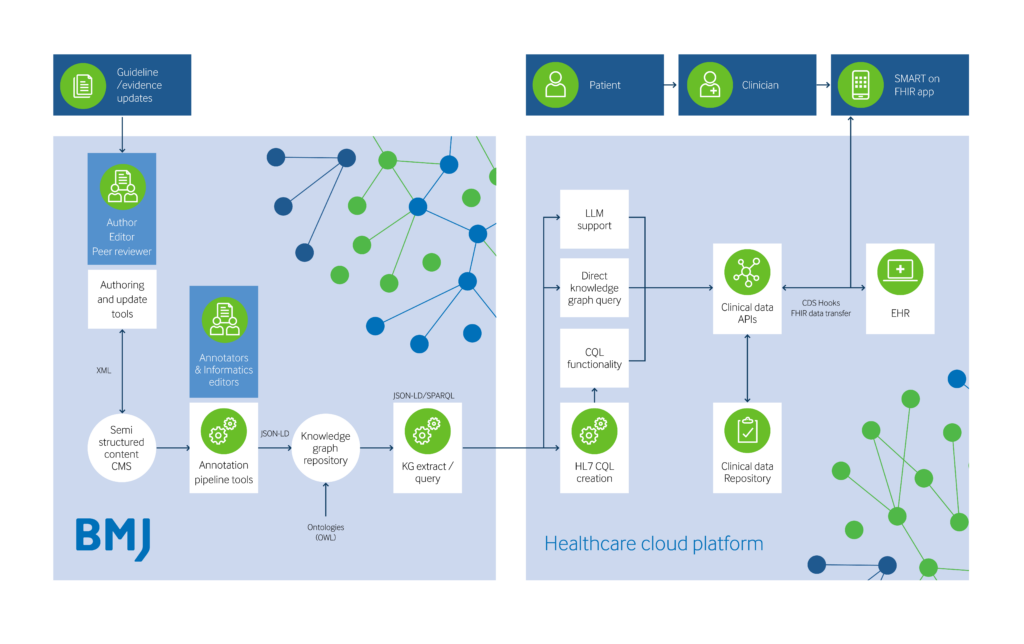
Knowledge graph (KG): A knowledge graph captures knowledge as a network of entities (or nodes) and relationships between them. It is a way of organizing information in a structured and computable way that places greater focus on the interconnections between entities which is a central feature of healthcare knowledge.
JSON-LD: Standard for exchanging knowledge graph information.
RDF/OWL: Ontology Web Language – standard for formal representation of concepts from resources such as SNOMED-CT. Concepts often form key nodes in a knowledge graph.
SNOMED-CT: Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine – Clinical Terms – global standard for healthcare terminology.
LLM: Large language model – An artificial neural network that has learned statistical relationships from a huge corpus of text documents. Acquire knowledge about syntax and semantics.
HL7: Health Level 7 – a series of standards for the transfer of clinical and administrative healthcare data.
EHR: Electronic Healthcare Record – the real time patient centered records.
HL7 FHIR: Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources – the latest generation of HL7 standards.
CQL: Clinical Quality Language – a healthcare domain specific technical language for encoding quality measures and clinical decision support logic.
SMART on FHIR: An HL7 standard that specifies how 3rd party apps for clinicians and patients can be launched from existing electronic healthcare record systems and clinical data repositories.
CDS hooks: An HL7 standard specifies how 3rd party apps can proactively provide support at various points in the clinician’s workflow.